How to Read an Ultrasound Picture
Ultrasound Imaging for Pregnancy
An ultrasound is a technique that produces 2D or 3D images of the inside of a patient’s body.
Specifically, pregnancy ultrasound images are a popular way to monitor a baby’s development. Ultrasound machines use sound waves to produce and display an image of the fetus inside the uterus.
Furthermore, they can also help monitor fetal position, movement, heart rate and more at different stages of pregnancy.
- Profile
- Face
- Spine
- Legs
- Placenta
- Umbilical Cord
- and more
Ultrasound Images at Different Pregnancy Stages
Visibility Scan
To start, the baby’s bones and organs begin to develop in the First Trimester.
Generally, the fetus will look like a tiny human being and a heartbeat even can be heard. Particularly, ultrasounds between 6 to 8 weeks check for:
- growth of the embryo
- gestational age
- estimated delivery date (EDD)
- and more

Fetal Anatomy Scan
Then, the baby’s anatomy becomes visible in the Second Trimester.
Most importantly, Sonographers will likely be able to see the baby’s genitals to determine gender. Specifically, ultrasounds between 18 and 22 weeks examine:
- amount of amniotic fluid
- fetal height and weight
- the placenta
- and more
Fetal Non-Stress Test
Finally, the baby’s vital organs are nearly fully developed in the Third Trimester.
However, ultrasounds at this time are only recommended for high risk pregnancies. Evidently, Fetal Non-Stress Tests between 26 and 30 weeks monitor:
- fetal heart rate
- fetal movement
- contractions
- and more
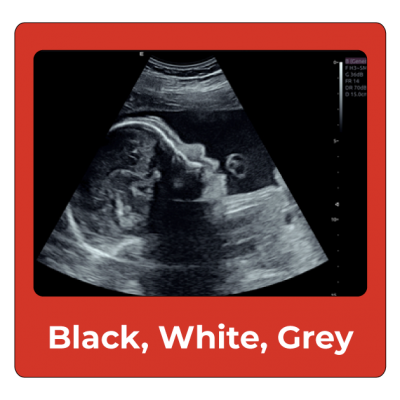
Colors on Ultrasound: Black, White and Gray
Most 2D Ultrasound images are captured in black and white. The various shades of black, white and even gray can tell users the density of the tissue that the sound waves pass through.
The denser the tissue, the brighter it will appear on an ultrasound.
- Black: Amniotic Fluids in the uterus
- White: Bones of the fetus, such as ribs or the spine.
- Gray: Tissue, such as dense uterine tissue.
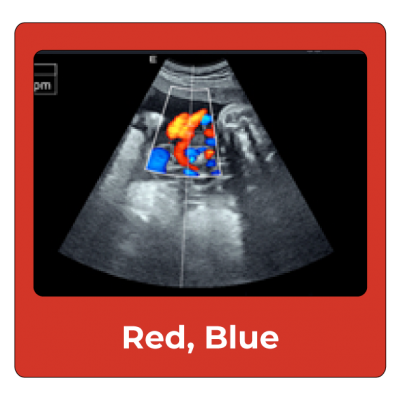
Colors on Ultrasound: Red and Blue
Color dopplers allow medical providers to observe the direction and speed of blood flow in a fetal heart. So, what do red and blue mean on an ultrasound? Contrary to popular belief, red and blue do not directly represent veins and arteries.
- Red: represents blood moving towards the probe
- Blue: represents blood moving away from the probe
Seeing them both in conjunction can show that each side of the heart to ensure proper function.