Defibrillator vs. Pacemaker: What’s the Difference?
Introduction
Irregular heartbeats, or arrhythmias, that are above or below the normal range can negatively affect the quality of life for many patients. Thankfully, pacemakers and defibrillators are life-saving medical devices that help correct heartbeats that are too slow or too fast. Historically, these devices have been reliable, with a reported mechanical failure of less than one out of 1,000.
Both pacemakers and defibrillators regulate heartbeats back to a normal pace. However, they have different functions and applications. In this article, we’ll break down both devices, their uses, and specify the key differences between them.
What is a Pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a device that monitors heart rate and helps the heart beat in a normal rhythm, typically when the heartbeat is too slow (under 60 BPM). Patients who have a very slow heart rate can experience fatigue, dizziness and shortness of breath.
To combat this, pacemakers send steady, low-energy electrical pulses to the heart at a pacing rate. Patients often describe these sensations as a non-painful, fluttering feeling in the chest.
Different Types of Pacemakers
Doctors will usually perform a diagnostic evaluation and recommend the right pacemaker based on your specific heart conditions. There are 3 types of internal pacemakers.
Single-lead pacemakers have one lead connected to either the heart’s right ventricle or right atrium.
Double-lead pacemakers have two leads connected to the heart’s right ventricle and right atrium.
Biventricular pacemakers have three leads connected to the heart’s right atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle.
What is a Defibrillator?
A defibrillator is a device that monitors and helps the heart beat in a regular rhythm, typically when the heartbeat is too fast (over 100 BPM). However, defibrillators are primarily used to shock a person’s heart when the rhythm becomes dangerously abnormal.
Additionally, defibrillators are capable of sending high-energy electrical shocks in the event of cardiac arrest. Patients often describe these sudden jolts as a kick to the chest.
Different Types of Defibrillators
There are three types of defibrillators: ICDs, AEDs and WCDs. While all have the same function, the devices themselves are used in different situations.
An ICD is a small battery-powered device that is surgically placed in the chest area. Specifically, it continuously monitors the heart beat and automatically delivers shocks to restore a regular heart rhythm.
An AED is an external defibrillator system for people experiencing cardiac arrest. Generally, this system uses pad electrodes that attach to the chest of the affected person.
Most importantly, AED’s are often found in public spaces including: schools, shopping malls, groceries stores and airports. For more information on how to use AED’s, click here.
A WCD is a wearable vest that has sensors that attach to the skin. It is worn under a patient’s clothes and is programmed to detect a particular heart rhythm.
Typically, WCD’s are used for patients who are at risk of arrhythmia for a temporary period.
What Are the Differences Between a Pacemaker and a Defibrillator?
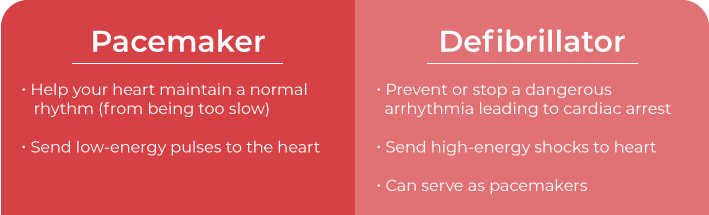
While pacemakers and defibrillators are similar devices, they have distinct purposes that are important to know, especially if you suffer from any heart conditions.
Pacemakers help your heart maintain a normal rhythm, specifically from being too slow. They accomplish this by sending low-energy pulses to the heart. Defibrillators help prevent or stop a potentially dangerous arrhythmia that could lead to sudden cardiac arrest. They send high-energy shocks to the heart to reset the rhythm.
Defibrillators can serve as pacemakers, but pacemakers cannot serve as defibrillators.
Closing
To recap, defibrillators and pacemakers are devices used to help conditions like arrhythmia and heart failure.
On one hand, pacemakers pace your heart rate if it is too slow. On the other hand, defibrillators pace your heart rate if it is too fast. Additionally, defibrillators can deliver high-energy shocks in the event of heart failure. So, if you’re looking for AED’s with defibrillator and pacemaker capabilities, click here to view our most popular offerings.
Citations
https://www.okheart.com/about-us/ohh-news/pacemaker-or-defibrillator-what%E2%80%99s-the-difference
https://www.healthline.com/health/arrhythmia/defibrillator-vs-pacemaker#defibrillator
https://www.sutterhealth.org/ask-an-expert/answers/pacemaker-vs-defibillator
https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/how-aeds-public-places-can-restart-hearts
https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-treatments/p/pacemaker/types.html







