How to Interpret a Spirometry Test

What is a Spirometry Test?
Spirometry is a test that doctors use to asses how well your lungs are working. Spirometers are used to detect lung function abnormalities. They are also used to diagnose obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
Often, doctors recommend spirometry tests for patients with shortness of breath, a dry cough or other common symptoms.
Obstructive Lung Diseases
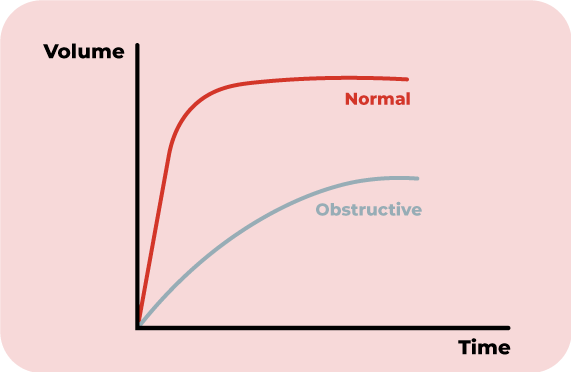
Generally, people with Obstructive Lung Diseases typically have difficulty exhaling air out of their lungs. As a result, air is either exhaled slower than normal, or a significant amount of air will still reside in the lungs.
For example, asthma, COPD and chronic bronchitis are common obstructive lung diseases.
Restrictive Lung Diseases
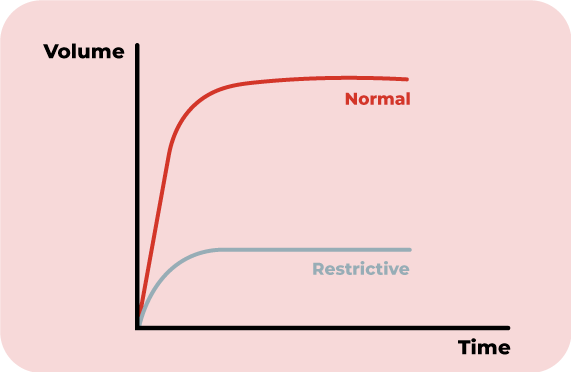
On the other hand, people with Restrictive Lung Diseases typically have difficulty inhaling air into their lungs. In other words, they cannot fully fill their lungs with air.
For example, pulmonary fibrosis is a common restrictive lung disease.
What does a Spirometer Measure?
A spirometer is a small medical device that records the volume and flow of air through the lungs.
In particular, spirometers measure 2 parameters that are essential for evaluating lung health and diagnosing lung diseases. These include: FVC and FEV1. Doctors will then use these measurements to determine the FEV1/FVC ratio. Let’s explain.
FVC
FVC, or Forced Vital Capacity represents the total amount of air (measured in liters) a person can exhale following a deep inhalation. An abnormal FVC can be an indicator of a restrictive lung diseases.
FEV1
FEV1, or Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second represents the amount of air a person can force out in one second following a deep inhalation. An abnormal FEV1 can be an indicator of an obstructive lung disease.
FEV1/FVC Ratio
FEV1/FVC Ratio is the percentage of the total amount a person can exhale in one second.
- A low FEV% is indicative of an obstructive lung disease
- A high (or normal) FEV% can be suggestive of a restrictive lung disease.
How is a Spirometry Test Performed?
According to the American Lung Association, spirometry tests take about 30 to 45 minutes. In addition, the tests may be repeated up to three times for the most accurate results. Here is a general overview of a spirometry test procedure.
- First, a doctor or nurse will place a clip on the patient’s nose to prevent breathing through the nostrils.
- Next, the medical provider will give the patient a mouthpiece connected to a spirometer.
- Then, the patient will take a deep breath and exhale into the mouthpiece. Most importantly, patients should exhale as hard and as fast as possible for best results. Repeat three times.
- Finally, doctors will interpret test results, and provide a diagnosis.

How to Interpret Spirometry Test Results
Here is a step by step instruction on how to interpret spirometry test results. With it, you can determine if a respiratory disease is present. Refer to the normal values table below.
- To start, take a look at the FVC, and check if it is within the normal or abnormal range.
- Next, look at the FVE1, and check if it is within the normal or abnormal range.
- Afterwards, calculate at the FEV1/FVC, and check if it is within the normal or abnormal range.
According to the table, the predicted percentages for FVC and FEV1 should be above 80% for normal lung function health. Similarly, the FEV1/FVC should be above 70% for normal lung function health. If any of these measurements are considered abnormal, Doctors can make accurate diagnoses and start treatment.
Spirometry Normal Values
Normal results for a spirometry test vary based on a number of factors. Specifically, these include a patient’s: age, height, race and sex.
Normal Value for FVC:
- Healthy: 80% or above
Abnormal Values for FVC:
- Mild: 70 to 79%
- Moderate: 60 to 69%
- Severe: <60%
Normal Value for FEV1:
- Healthy: 80% or above
Abnormal Values for FEV1:
- Mild: 70 to 79%
- Moderate: 60 to 69%
- Severe: <60%
Normal Value for FEV1/FVC:
- Healthy: 70% or above
Abnormal Values for FEV1/FVC:
- Mild: 60 to 69%
- Moderate: 50 to 59%
- Severe: <50%







