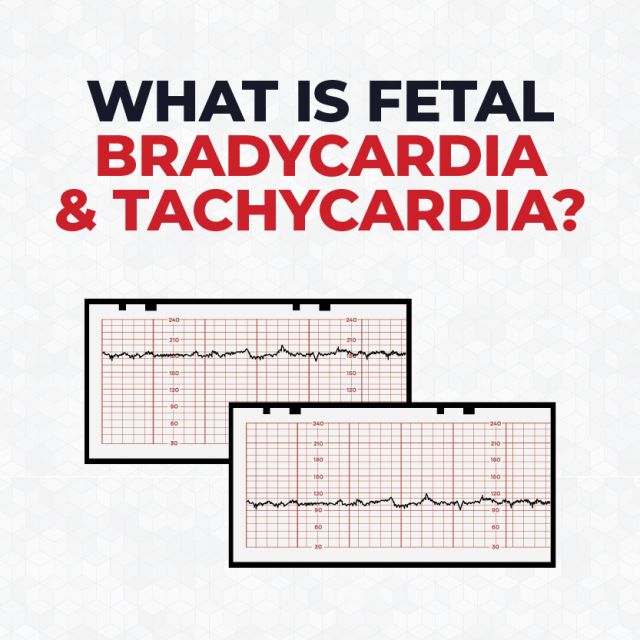
What are the Risks and Limitations of Fetal Heart Monitoring?

Introduction
Fetal heart monitoring is a common procedure used during pregnancy and labor to monitor the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions. While it is a valuable tool for assessing fetal well-being, there are risks and limitations associated with both external and internal monitoring methods.
Fetal monitoring, while generally considered safe, does carry some risks. In this article, we’ll go over some potential risks and limitations of fetal monitoring tests.
External and Internal Fetal Monitoring Risks and Limitations
Discomfort
Invasive fetal monitoring techniques, while essential for monitoring the health and well-being of the fetus during labor and delivery, can cause discomfort for the mother. Some of the ways invasive monitoring techniques lead to discomfort include:
Physical Discomfort during Placement: The insertion of invasive monitoring devices, such as fetal scalp electrodes or intrauterine pressure catheters, can cause discomfort or pain for the mother.
Sensation of Pressure or Irritation: Once in place, invasive monitoring devices may cause a sensation of pressure or irritation for the mother. This sensation may intensify during contractions or movement.
Inaccuracies
While external fetal monitoring is a widely used method for assessing fetal well-being during labor and delivery, it can sometimes lead to inaccuracies for the various reasons:
Positioning: The accuracy of external fetal monitoring relies on correct placement of the monitoring devices on the mother’s abdomen. If these devices are not positioned accurately or if there is movement, the signals received might be distorted.
Maternal Movement: Maternal movement can cause fluctuations in the signals received by the monitoring device. This movement can interfere with the accuracy of the readings, making it difficult to interpret fetal heart rate patterns correctly.
Signal Interference: External fetal monitoring can be susceptible to interference other monitoring devices, or noise in the environment. This interference can distort the signals and lead to inaccuracies in the readings.
Injuries and Infections
Invasive monitoring techniques, such as fetal scalp electrodes or intrauterine pressure catheters are generally safe when performed by trained healthcare professionals. However, they do carry some risks, including injuries and infections. Here’s how:
Conclusion
While fetal heart monitoring is a valuable tool in obstetric care, it’s important to be aware of its limitations and potential risks. Healthcare providers should carefully consider individual patient factors and preferences when making decisions about obstetric management.